Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Basal Insulin
Download File
Objective
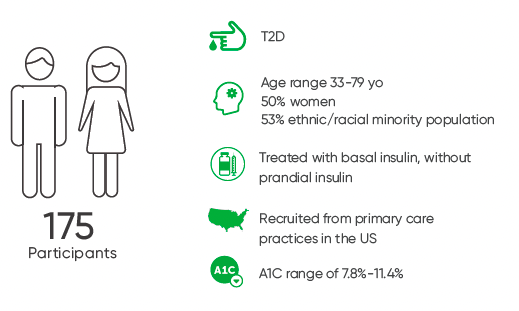
To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of CGM in older adults with type 2 diabetes treated on basal insulin only in a post-hoc analysis of the MOBILE study.
Study Outcomes Measured
The primary outcomes measured were A1C, time in target glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL, time with glucose level at ≥250 mg/dL, and mean glucose level at 8 months.
Results
- Primary outcome was the -1.08% reduction in A1C among CGM group in both age cohorts, compared to the Blood Glucose Monitoring (BGM) group, that had mean reductions of -0.38% for those ≥65 years*, and -0.73% for those <65 years.**
- Participants ≥65 years on CGM had a mean increase in Time in Range (TIR) of 16% compared to their baseline levels, whereas the BGM group exhibited a mean TIR change of -5%. Adjusted difference, 19% (P<0.01).
Key Takeaways
- Use of CGM is associated with greater A1C decrease than BGM alone in adults with T2D on basal insulin, regardless of their age.1,2
- Using CGM is beneficial for adults aged 65 and above who have type 2 diabetes (T2D) and struggle to control their glucose levels using only basal insulin.2
- The improvements in glucose control seen with CGM are just as significant in older adults as they are in younger ones.1
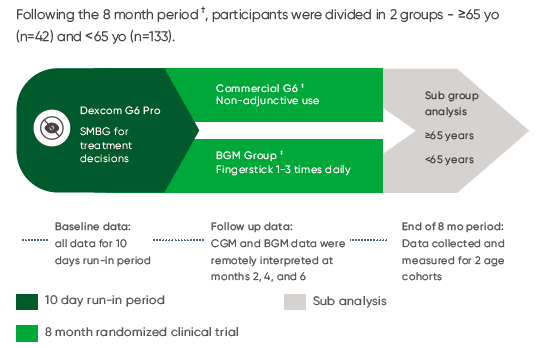
* adjusted difference= -0.65% (95% CI -1.49, 0.19) (p=0.13) ** adjusted difference= -0.35% ( 95% CI -0.77, 0.07) (p=0.10)
† A1C was collected at randomization, month 3, and month 8 and measured at a central laboratory
‡ Participants in the CGM group wore the device continuously up through 8 months, whereas participants in the BGM group wore a blinded CGM during the 10 days after the 3-month visit and 10 days leading up to the 8-month visit.
1. Bao S, Bailey R, Calhoun P, Beck RW. Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Basal Insulin. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022 May;24(5):299-306. doi: 10.1089/dia.2021.0494.
2. Martens T, et al; MOBILE Study Group. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Basal Insulin: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Jun 8;325(22):2262-2272. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.7444. PMID: 34077499; PMCID: PMC8173473